Dell OptiPlex 3050 Micro
Contents
PLEASE READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE INSTALLING, OR YOU MAY BRICK YOUR MACHINE!! - Please click the link and follow the instructions there, before flashing. For posterity, here is the link again.


| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Dell |
| Name | OptiPlex 3050 Micro |
| Variants | OptiPlex 3050 Micro |
| Released | 2017 |
| Chipset | Intel Kaby Lake |
| CPU | Intel Kaby Lake |
| Graphics | Intel HD graphics |
| Memory | DDR4 SODIMMs (max 32GB, 2x16GB) |
| Architecture | x86_64 |
| Original boot firmware | Dell UEFI firmware |
| Intel ME/AMD PSP | Present. Can be disabled with me_cleaner. |
| Flash chip | SOIC-8 16MiB (128Mbit) |
W+: Works without vendor firmware;
N: Doesn't work;
W*: Works with vendor firmware;
U: Untested;
P+: Partially works;
P*: Partially works with vendor firmware
?: UNKNOWN AT THIS TIME
| Features | |
|---|---|
| Internal flashing with original boot firmware | W* |
| Display (if Intel GPU) | W+ |
| Audio | W+ |
| RAM Init | W* |
| Payloads supported | |
|---|---|
| GRUB (libgfxinit only) | Works |
| SeaBIOS | Works |
Dell OptiPlex 3050 Micro is available to purchase with Libreboot preinstalled. See: https://minifree.org/product/libreboot-3050-micro/
Introduction
Unavailable in Libreboot 20240612 or earlier. You must compile from source, or use a version newer than Libreboot 20240612.
Official information about the computer can be found here: https://www.dell.com/support/manuals/en-uk/optiplex-3050-micro/optiplex_3050-mff_om/processor-specifications?guid=guid-8ca53ab2-a85d-42d5-9106-5214220306aa&lang=en-us
Warning regarding NVMe SSDs
Please use at least Libreboot 20241206 revision 3 or higher. This is because older revisions contained a bug, where the NVMe SSD would be replugged under Linux, randomly, leading to data loss.
This is fixed in 20241206 rev3 or higher, by disabling PCI-E hotplug on the NVMe SSD slot.
See: Libreboot 20241206 release
Build ROM image from source
The build target, when building from source, is thus:
./mk -b coreboot dell3050micro_vfsp_16mb
Mate Kukri’s deguard utility disables the Intel Boot Guard on this
machine. Libreboot uses this by default, along with me_cleaner to provide
a neutered ME setup; unlike on other platforms, arbitrary code execution is also
possible inside the ME on this mainboard, giving it much higher potential for
software freedom in the future.
Issues
This machine basically works flawlessly, as of the Libreboot 20241206 release. All the initial bugs were fixed, e.g. PWM fan control works now. A very nice machine, and inexpensive, plus very easy to set up for the average user. The ideal Libreboot desktop.
Note that HDMI audio does work, but you have to select it in your audio
server e.g. pipewire. The pavucontrol utility in Linux (with pipewire) lets
you have a lot of control over audio I/O. Libreboot patches the board to add
a verb, so headphones should work.
Selection of audio devices and outputs is a bit idiosyncratic on this board. Just play with pavucontrol for your setup and it should work fine.
Installation
Insert binary files
If you’re using a release ROM, please ensure that you’ve inserted extra firmware required refer to the guide for that. (failure to adhere to this advice will result in a bricked machine)
Libreboot’s build system automatically downloads and processes these files if you build Libreboot from source, but the same logic that it uses must be re-run if you’re using a release image.
Of particular interest, this board uses the deguard software, to disable Intel Boot Guard. This means also that the ME firmware no longer has functional cryptographic signature checking for most of it; you can theoretically run whatever you want on the ME coprocessor.
Libre ME doesn’t exist yet, but it’s now possible. Example use-case for a libre ME could include, for example, running an out-of-bound packet filter on a secure network (with flash write protection, making it invincible to any OS-based software attacks).
MAC address
This has a realtek NIC inside, instead of Intel, so the MAC address will not change. This means: there is no GbE region in the flash.
You can still use something like GNU MAC Changer to change your MAC address from Linux if you want to.
This is great, because that’s one less complexity to deal with during installation.
Flash a ROM image (software)
If you’re already running Libreboot, and you don’t have flash protection turned on, internal flashing is possible.
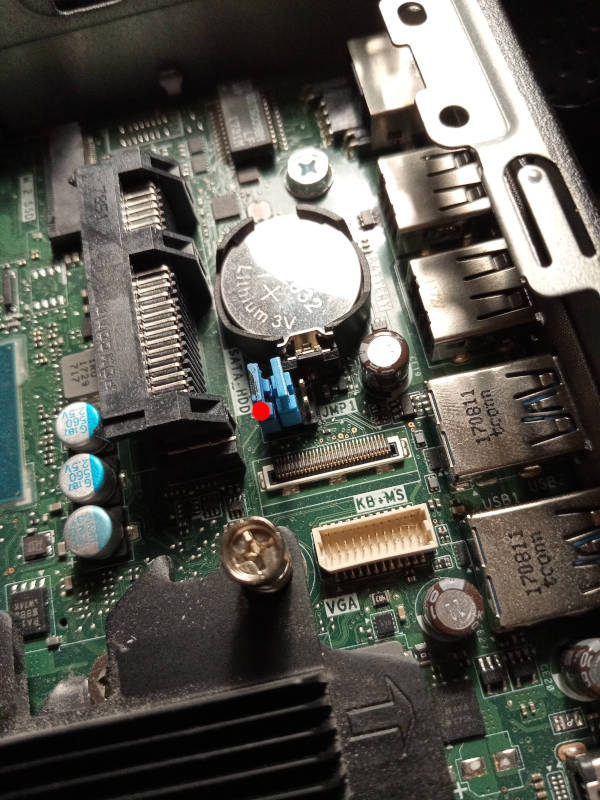

If you have factory firmware (Dell), you can short the service jumper. It’s
near the RAM, under where the HDD goes (click the photos shown above).
Just put a short on it when booting,
and all flash protection is disabled; the factory firmware write might EFI
variables to flash during shutdown sequence, so you should pull the plug to
shut it down (remove the power by pulling the plug) after flashprog
says VERIFIED.
Flash a ROM image (hardware)
For general information, please refer to 25xx NOR flash instructions - that page refers to use of socketed flash.
The side cover comes off easily, and you can find the flash ICs next to the RAM. Simply remove the screw at the back. The top panel then slides forward, and you can remove the SSD caddy; from then on, the flash is accossible.
Observe the following photo of the flash (SOIC-8):
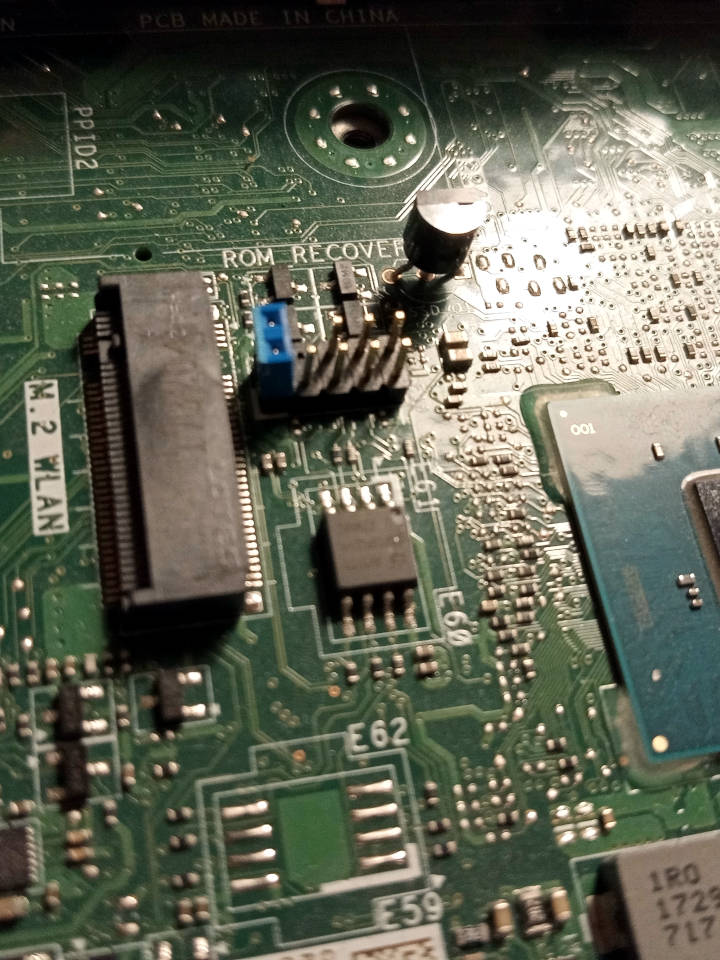

You can otherwise flash internally, including from factory firmware(if the service jumper is set).
Errata
Power-on after power failure
Older Libreboot revisions made this machine always turn on, when plugging in a power supply (charger brick), if a previous power loss was observed. This is because coreboot sets a special register in the PMC that configures such behaviour, but it was hardcoded to always-on. This is undesirable for most people, so Libreboot 20241206 revision 8 and newer releases contain the following modification:
https://browse.libreboot.org/lbmk.git/commit/?id=09a01477df67e3ddc36e11123c537332d7813c50
If you wish to modify this behaviour again, you could modify the patch
referenced there; the actual location of the .patch file may change over
time, so you can basically just modify the coreboot source file
at src/soc/intel/common/block/pmc/pmclib.c (for the coreboot tree
under src/coreboot/ in lbmk, pertaining to your board, which can be determined
by reading the tree variable in your board’s target.cfg file within lbmk).
Use the patch as reference, to modify the coreboot behaviour as you wish, and re-compile from source.
TPM disabled
The TPM is disabled on this device, to prevent hanging/boot delay in SeaBIOS, due to buggy TPM drivers there.
Legacy 8254 timer
Legacy 8254 timer enabled in coreboot, to prevent SeaBIOS from hanging.
HyperThreading on 3050 Micro
Also called SMT. This is a feature where you get 2 threads on a single core. It can improve performance in some workloads, but is actually a performance liability in others, depending on your OS kernel/scheduler and the actual workload.
It is a security liability, due to the Spectre/Meltdown attacks, so we recommend turning it off, at the very least from your running operating system. On this platform, you can easily turn it off from coreboot.
Libreboot disables HyperThreading by default, from Libreboot 20241206 rev8 onward, on this board. To turn it back on, please build from source and before running the build command, do this:
./mk -m coreboot t480_vfsp_16mb # replace t480 with t480s if needed
In the menu that appears, go Chipset -> Enable Hyperthreading and turn it on. Then exit from the menu, saving the config where prompted. You will see this menu twice, because there are two configs for each of these boards.
SMT is rarely of benefit in practise, but can be useful in some circumstances. For example, if you’re compiling a large codebase from source that takes hours, SMT increases the building speed by about 15 percent; for example, a 3 hour build job might take about 2 hours and 40 minutes instead.